The Chemistry of Hand Warmers

Hand warmers are a great application of chemistry and controlled reactions.
Table of Contents
Hello everybody! I have been busy this winter having the opportunity to participate in many chemical experiments and other experiences, but now I’m back!
It is still winter, but now it’s February, the coldest month of winter. If you are freezing, you have come to the right place! Today we will be talking about the chemistry of hand warmers!
Hand Warmers and … more Hand Warmers
Before we begin, you should know that there is not one type of hand warmer. Different types of hand warmers work through different types of changes, either physical or chemical.
However, all hand warmers revolve around one underlying principle: enthalpy.
What is Enthalpy?
Enthalpy is a measure of the amount of heat energy in a system. The system is whatever is undergoing a physical or chemical change, whether it be wood burning into ash or ice melting into water that annoyingly dilutes your glass of soda. The change in enthalpy is simply a measure of the amount of heat energy transferred from or to the system.
The symbol for the change in enthalpy is ΔH. If ΔH is positive for a system, it means whatever change is occurring to the system is causing the system to absorb heat energy from its surroundings, making the system feel cold to the touch. A negative ΔH means that the change to the system is causing the system to release heat energy into its surroundings, making the system feel warm to the touch. Changes that cause a positive ΔH are called endothermic changes, and changes that cause a negative ΔH are called exothermic changes.
For example, water evaporating into water vapor is an endothermic change. To turn water into water vapor, virtually all the attraction between the water molecules in the water must be overcome, which requires the water to absorb heat energy from its surroundings.
Now let’s apply the concept of enthalpy to hand warmers!
Air-Activated Hand Warmers
To warm your hands, air-activated hand warmers use an exothermic chemical reaction. That is, the components inside the hand warmer react with each other, breaking and forming bonds to release heat energy. Breaking bonds requires absorbing heat energy and forming bonds releases heat energy. Exothermic chemical reactions are chemical reactions where the heat energy released by the formation of bonds is more than the absorption of heat energy through the breakage of bonds, causing a net release of heat energy.
The specific exothermic chemical reaction in question is the rusting of iron; Iron reacts with oxygen in the air to form ferric oxide, commonly known as rust.
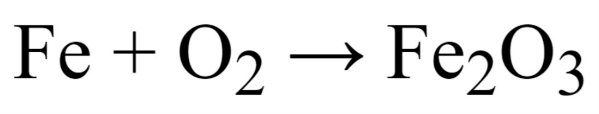
The unbalanced chemical equation for iron rusting.
The rusting process is slow, so air-activated hand warmers use water and salt to speed up the rusting process. A simplified diagram of an air-activated hand warmer is shown below:
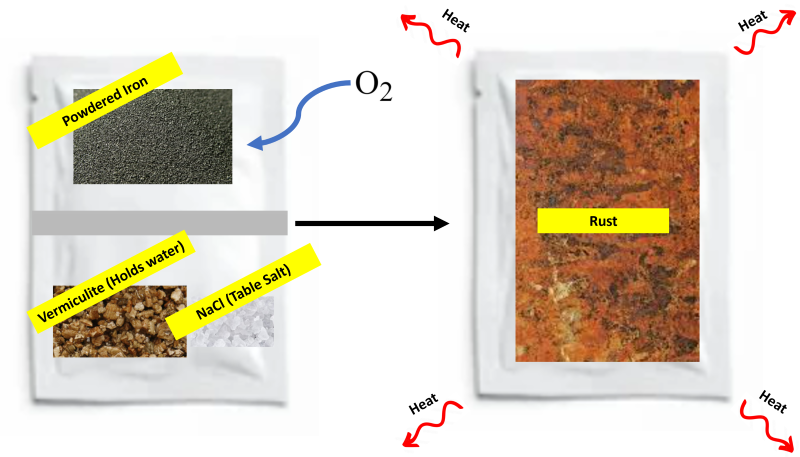
The grey barrier is broken to combine the components of the hand warmer.
Combustion Hand Warmers
Combustion hand warmers use an exothermic reaction called combustion, commonly called burning, to provide warmth. Combustion hand warmers fall into two main categories: lighter fluid hand warmers and charcoal hand warmers.
Lighter Fluid Hand Warmers
Lighter fluid hand warmers involve the combustion of lighter fluid with the addition of a catalyst. The catalyst allows for the combustion reaction to occur at a temperature low enough to prevent a fire.
The lighter fluid and catalyst are placed in a small metal container and then lit to initiate the combustion reaction. Then, the metal container is covered to prevent hand burns from usage of the hand warmer.

The advantage of such a warmer is that it is one of the best hand warmers in terms of amount of warmth provided and duration of warmth provided. Furthermore, the covered metal container can be used indefinitely. While the catalyst – which might contain the rare metal platinum – does not last forever, the catalyst is small and can last for years before needing to be replaced.
The main problem with lighter fluid hand warmers is that burning lighter fluid, a gas commonly known as petroleum naphtha, contributes to global warming; reuse of the hand warmer requires refueling it with lighter fluid.
Charcoal Hand Warmers
Charcoal hand warmers consist of a covered metal container; the cover is to prevent hand burns from usage of the hand warmer. A charcoal stick is lit on both ends and then extinguished, causing smoldering of the charcoal. The charcoal is then placed in the covered metal container.

While the charcoal hand warmer experiences the same benefits of the lighter fluid hand warmer on top of the low cost of charcoal sticks, it suffers from the same disadvantage of the lighter fluid: burning charcoal sticks, which must be replaced every time the hand warmer is reused, contributes to global warming.
Electric Hand Warmers
Unlike the hand warmers we have covered so far, electric hand warmers work using a physical process. Electric hand warmers consist of a circuit containing a battery and a conductive material that has a significant amount of resistance. The outer electrons of the atoms in the somewhat conductive material are free to flow around through the material, creating a “sea of electrons” and a lattice of cations (positively charged ions).
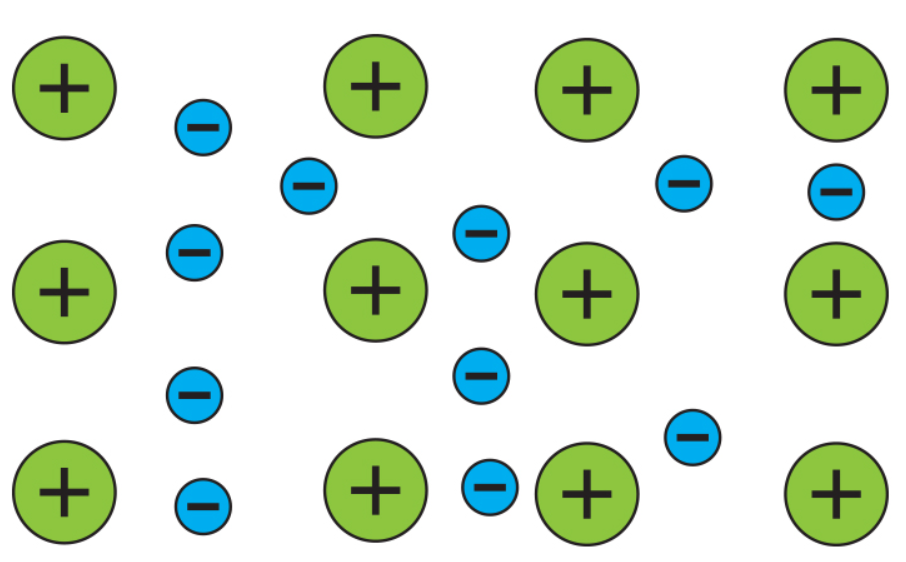
When the hand warmer is turned on, a current is produced, and the electrons start moving. As the electrons move, they bump into the cations. This bumping transfers kinetic energy, the energy an object has when it is moving, from the electrons to the cations, causing the cations to vibrate faster and faster. Since temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in an object, the conductive material heats up.

While electric hand warmers can be recharged, the battery of the electric hand warmer will slowly deplete after each recharge, eventually needing to be replaced.
Supersaturated Hand Warmers
I have been saving this one for last because it is my favorite type of hand warmer. Supersaturated hand warmers, like electric hand warmers, rely on a physical process of precipitation.
For all substances, there exists a point at which no more of a substance can be dissolved in a solvent; the resulting mixture is called a saturated solution. The amount of a substance that can be dissolved in a solvent before a saturated solution is achieved is the solubility of the substance.
Interestingly, the solubility of a solid or liquid substance increases as the temperature increases. This property of solubility can be utilized by creating a saturated solution (where the dissolved substance is either a solid or liquid) at a high temperature and then slowly cooling the saturated solution down to room temperature. This process creates a supersaturated solution, where the amount of substance dissolved in the solvent is greater than the solubility of the substance for that temperature.
A supersaturated solution is metastable, meaning that it is only stable if it is not subjected to any significant disturbances. If I disturbed a supersaturated solution by dipping a pencil into the solution, the substance will start precipitating out of solution until a saturated solution is achieved. As some of the substance precipitates, attractions between the precipitating substance molecules form, releasing heat energy. However, to precipitate, the precipitating substance molecules must absorb heat energy to overcome their attractions with solvent molecules. I should also mention that the solvent molecules that were once attracted to the substance molecules will form attractions with other solvent molecules, releasing additional heat energy in the process. To be exothermic, the precipitation process has to release more heant energy than it absorbs. Below is a video that demonstrates cool ways to disturb a supersaturated solution:
In most supersaturated hand warmers, a small metal disk is inside the supersaturated solution. The metal must be bent to disturb the supersaturated solution and cause some of the substance to precipitate out of the solution.
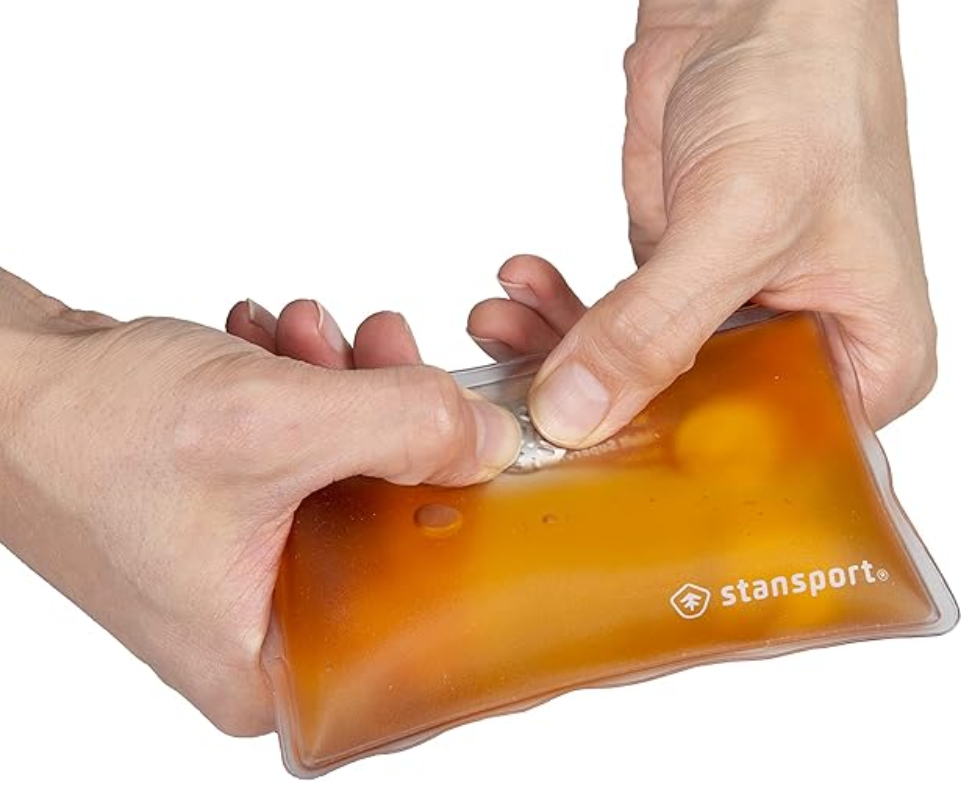

Also like electric hand warmers, supersaturated hand warmers are reusable. Once a supersaturated hand warmer has been used, heat the hand warmer in some boiling water so that the solubility of the substance increases, allowing for the precipitated susbtance to re-dissolve into the solvent. Once all of the precipitated substance has dissolved in the solvent, remove the hand warmer from the boiling water and let it cool to room temperature to create a supersaturated solution.
Now your supersaturated hand warmer is ready for re-use! Stay warm folks!